一天一个关于测试知识点,5分钟内讲解你最关心的软件测试问题,今天就接着来谈谈关于软件测试中的“UiAutomator API详解:UiDevice 类介绍”。

(1)获取UiDevice实例的方式。
在UiAutomation 2.0如下定义。
instrumentation = InstrumentationRegistry.getInstrumentation();
UiDevice.getInstance(instrumentation)
首先注册一个instrumentation实例,然后通过UiDevice的getInstance方法建立一个UiDevice类
案例4-2:获取UiDevice实例。
import android.support.test.uiautomator.UiDevice;
@Test
public void testHome()
{UiDevice.getInstance(instrumentation).pressHome();}
@Test
public void testMenu(){
UiDevice.getInstance(instrumentation).pressMenu();}
@Test
public void testRecent() throws InterruptedException,RemoteException {
UiDevice.getInstance(instrumentation).pressRecentApps();
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
(2)UiDevice的操作功能。
通过UiDevice可以。
l 获取设备信息,屏幕分辨率、旋转状态、亮灭屏状态等。
l 操作。按键、坐标操作、滑动、拖拽、灭屏唤醒屏幕、截图等。
l 监听功能。
手机上的按键包括。
HOME:主屏幕键。
MENU:菜单键。
BACK:返回键。
VOLUME_UP:音量加键。
VOLUME_DOWN:音量减键。
RecentApps:最近使用APP。
POWER:电源键。
Dpad:上下左右。
表4-3展示了所有的按键API。
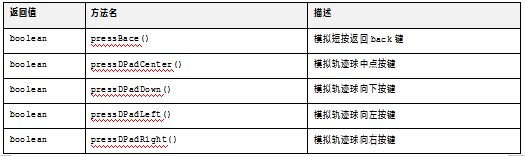
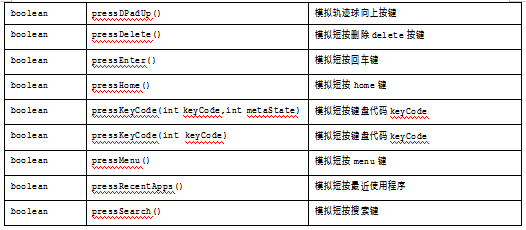
表4-3 UiDevice类提供的按键方法
案例4-3:UiDevice按键API。
import android.support.test.uiautomator.UiDevice;
@Test
public void testHome()
{UiDevice.getInstance(instrumentation).pressHome();}
@Test
public void testMenu(){
UiDevice.getInstance(instrumentation).pressMenu();}
@Test
public void testRecent() throws InterruptedException,RemoteException {
UiDevice.getInstance(instrumentation).pressRecentApps();
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
(3)KEYCODE键盘映射码,包括如下。
l KeyEvent:按键事件。
l META KEY。
l 辅助功能键:ALT、SHIFT、CAPS_LOCK。
KEYCODE键盘映射码见表4-4所示。
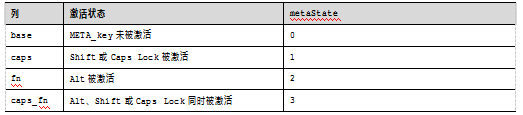
表4-4 KEYCODE键盘映射码
案例4-4:KEYCODE键盘映射码。
import android.view.KeyEvent;
…
@Test
public void testAndroidKey() throws UiObjectNotFoundException {
Util util=new Util();
util.comming("Demo4");
UiDevice.getInstance(getInstrumentation()).pressKeyCode(KeyEvent.KEYCODE_A);//小写a
UiDevice.getInstance(getInstrumentation()).pressKeyCode(KeyEvent.KEYCODE_B);//小写b
UiDevice.getInstance(getInstrumentation()).pressKeyCode(KeyEvent.KEYCODE_C);//小写c
UiDevice.getInstance(getInstrumentation()).pressKeyCode(KeyEvent.KEYCODE_A,1);//大写A
UiDevice.getInstance(getInstrumentation()).pressKeyCode(KeyEvent.KEYCODE_B,1);//大写B
UiDevice.getInstance(getInstrumentation()).pressKeyCode(KeyEvent.KEYCODE_C,1);//大写C
}
关于Util util=new Util()本节将会在后面介绍。
(4)坐标相关的知识
l 手机屏幕坐标:左上角开始到右下角结束。
l DP:设备独立像素,如320像素显示到640像素上要拉伸一倍。
l Point:代表一个点(x,y),左上角的坐标永远为(0,0)。
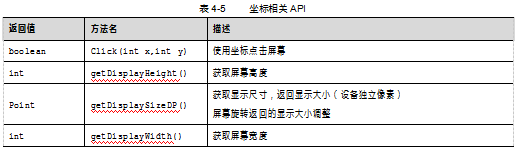
案例4-5:关于坐标的API。
@Test
public void testClick() throws UiObjectNotFoundException,RemoteException {
Util util=new Util();
util.comming("Demo4");
int h=UiDevice.getInstance(getInstrumentation()).getDisplayHeight();
int w=UiDevice.getInstance(getInstrumentation()).getDisplayWidth();
Point p=UiDevice.getInstance(getInstrumentation()).getDisplaySizeDp();
Log.i("AAA","The display width is: " + w);
Log.i("AAA","The display height is: "+h);
System .out.println(p);
UiDevice.getInstance(instrumentation).pressRecentApps();
UiObject recentapp = new UiObject(new UiSelector().resourceId("com.android.systemui:id/dismiss_task"));
Rect r = recentapp.getBounds();//获取控件对应的矩形区域相关属性
UiDevice.getInstance(getInstrumentation()).click(r.centerX(),r.centerY());
}
在这里的模拟器下运行上面程序,得到如下输出。
03-28 03:43:10.353 1675-1690/? I/AAA: The display width is: 320
03-28 03:43:10.354 1675-1690/? I/AAA: The display height is: 480
03-28 03:43:10.355 1675-1690/? I/System.out: Point(320,480)
可以获知,这个模拟器的分辨率为320×480。
其中。
l r.left :矩形左上角顶点X坐标。
l r.top :矩形左上角顶点Y坐标。
l r.right:矩形右下角顶点X坐标。
l r.bottom:矩形右下角顶点Y坐标。
l r.centerX():矩形的中心点X坐标。
l r.centerY():矩形的中心点Y坐标。
(5)拖曳与滑动
概念介绍。
l 拖曳:将组件从一个坐标移动到另一个坐标。
l 移动:从一个坐标点移动到另一个坐标点。
l 步长:从一点滑动到另一点使用的时间。
拖曳与滑动的相关API如表4-6所示。
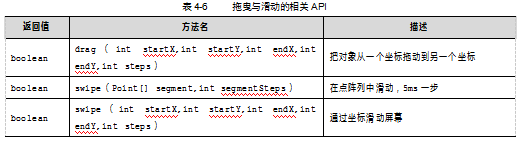
案例4-6:关于拖曳与滑动的API。
@Test
public void testDragAndSwipe() throws UiObjectNotFoundException {
Util util=new Util();
util.enterAPP();
UiObject recentapp1 = new UiObject(new UiSelector().text("Demo4"));
Rect r1 = recentapp1.getBounds();//获取控件对应的矩形区域相关属性
int startX,startY,endX,endY,steps;
startX=r1.centerX();
startY=r1.centerY();
endX=100;
endY=100;
steps=100;
UiDevice.getInstance(getInstrumentation()).drag(startX,startY,endX,endY,steps);
UiDevice.getInstance(instrumentation).pressHome();
recentapp1 = new UiObject(new UiSelector().text("Demo4"));
r1 = recentapp1.getBounds();//获取控件对应的矩形区域相关属性
startX=r1.centerX();
startY=r1.centerY();
endX=UiDevice.getInstance(getInstrumentation()).getDisplayWidth()/2;
endY=48;
steps=100;
UiDevice.getInstance(getInstrumentation()).swipe(startX,startY,endX,endY,steps);
Point p1=new Point();
Point p2=new Point();
Point p3=new Point();
Point p4=new Point();
p1.x=100;p1.y=100;
p2.x=100;p2.y=300;
p3.x=300;p3.y=300;
p4.x=300;p4.y=100;
Point[] ps={p1,p2,p3,p4,p1};
UiDevice.getInstance(getInstrumentation()).swipe(ps,50);}
关于方法enterAPP()将在后面进行介绍。
(6)屏幕旋转
屏幕旋转相关知识。
l 旋转方向:0°、90°(向左转)、180°、270°(向右转)。
l 重力感应器:重力感应器是旋转所依靠的。
l 固定位置:指将屏幕方向固定在0°、90°或者180°等。
l 物理旋转:物理旋转与重力感应器关联在一块,关闭物理旋转就是关闭了重力感应器,反之亦然)。
旋转屏幕相关API见表4-7所示。
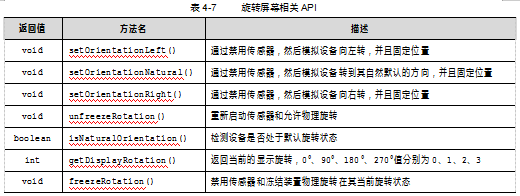
案例4-7:关于屏幕旋转的API。
@Test
public void testDemo5() throws UiObjectNotFoundException,RemoteException,InterruptedException {
Util util=new Util();
util.comming("Demo5");
UiObject myroot=new UiObject(new UiSelector().className("android.view.View").instance(0));
myroot.click();
myroot.click();
int r = UiDevice.getInstance(getInstrumentation()).getDisplayRotation();
if (r == 0) {
Log.i("AAA","r=" + r);
UiDevice.getInstance(getInstrumentation()).setOrientationLeft();}
if (r == 1) {
UiDevice.getInstance(getInstrumentation()).setOrientationNatural();
Thread.sleep(1000);
UiDevice.getInstance(getInstrumentation()).setOrientationLeft();}
if (r == 2) {
UiDevice.getInstance(getInstrumentation()).setOrientationNatural();
Thread.sleep(1000);
UiDevice.getInstance(getInstrumentation()).setOrientationLeft();}
if (r == 3) {
UiDevice.getInstance(getInstrumentation()).setOrientationNatural();}}
(7)灭屏和唤醒
l 灭屏:将屏幕按电源键处于锁屏状态。
l 唤醒:唤醒处于灭屏状态的设备。
UiAutomation提供了如下关于灭屏和唤醒的API,如表4-8所示。
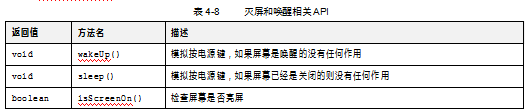
(8)等待
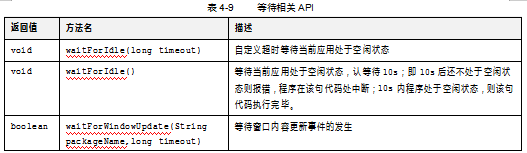
由于对于GUI功能测试程序,界面元素需要加载的,有一定的延时,好些测试代码运行失败往往不是系统功能出现了问题,而是元素没有加载上来,所以找不到元素。可以使用Java提供的Thread.sleep(4000);进行死等待,也可以通过UiAutomation提供的等待API,如表4-9所示。
(9)截图
截图也是在功能自动化测试中经常会用到的技术,比如在系统出现异常的时候往往想知道系统当时的界面是什么样的状态,在这里就可以用到截图。关于截图需要明确下面几个概念。
l 图片缩放比例:如缩小1/2,即将100px×100px的图片长宽都缩小为原来的1/2,50×50px。
l 图片质量:一般是指图片的大小,质量越高图片越大。
l File 类:文件或者文件夹。
l 图片格式 :截图的格式都是PNG。
l 空闲状态:窗口没有更新或界面无动作。
关于截图的API见表4-10所示。
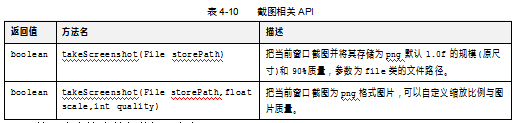
这两个方法中的参数如下定义。
l storePath:存储路径,必须为png格式。
l scale:缩放比例,1.0为原图。
l quality:图片压缩质量,范围为0-100。
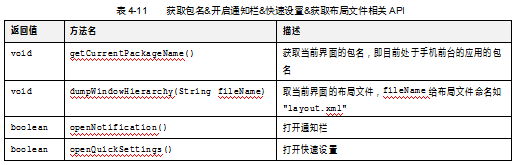
(10)获取包名&开启通知栏&快速设置&获取布局文件
l 包名:应用程序的Class名称,是应用的唯一标识。
l 布局:获取开发安卓程序中的layout.xml文件,定义界面的布局。
l 通知栏:从手机顶部下滑,出现的下拉界面即通知栏。
l 快速设置:即通知栏中的快速设置控件,快速设置界面可设置网络、屏幕亮度、飞行模式等。
UiAutomation提供了如下四个API,如表4-11所示。
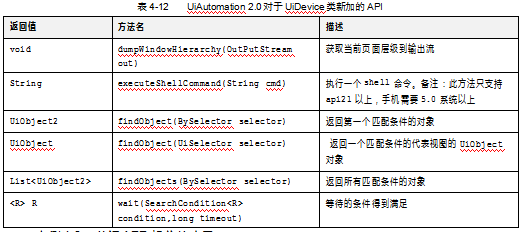
另外在UiAutomation 2.0对于UiDevice类还提供了如下六个API,见表4-12。
案例4-8:关闭APP操作的应用。
@Test
public void testDemo5() throws UiObjectNotFoundException,RemoteException,InterruptedException {
Util util=new Util();
util.comming("Demo5");
UiObject myroot=new UiObject(new UiSelector().className("android.view.View").instance(0));
…
UiDevice.getInstance(getInstrumentation()).executeShellCommand("am force-stop UiDevice.getCurrentPackageName()");
}
这个命令在旧版本的Android手机上不起作用。