本章主要讲解性能测试中如何用DTA调校索引,首先,Database Engine Tuning Advisor是一个物理数据库设计工具,它是建立在SQL Server 2000的Index Tuning Wizard的技术上,并取而代之,它接收形式为包含一组Select、delete、update语句的T-SQL脚本的工作负荷或SQL Profiler跟踪作为输入,而且会输出一个由对索引、索引的视图和统计进行创建、删除和划分的建议组成的T-SQL脚本,它还会给出性能改进的估计,DTA的结构图如图11-42所示。
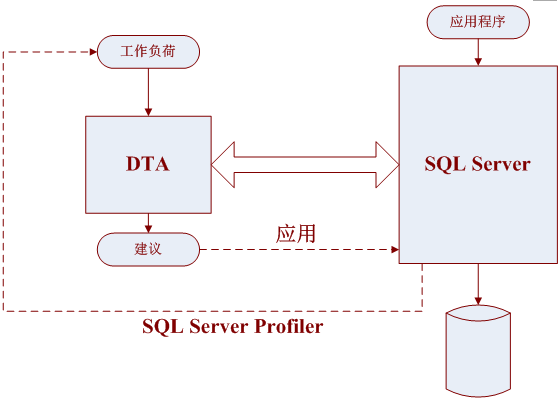
图11-42 DTA结构图
DTA可以对单个查询进行分析也可以对SQL Server Profiler Trace文件进行分析,分析后DTA会显示优化查询性能的建议,根据DTA提供的优化建议可以对查询语句进行优化,优化后再次对查询进行度量,直到达到性能要求为止。
对单个查询进行调校,包含两个步骤,一是统计查询执行期间的等待时间;二是使用DTA进行调校;
在开始调校之前,需要捕获开始度量,为了得到一致的结果,需要捕获一个冷时间和多个热时间并对这些热时间求平均值。冷时间是指SQL Server第一次运行一个查询所需要的时间,执行计划和数据不在缓存中,因此所有的工作必须从零开始,查询后续运行将会由于缓存的缘故快很多(已热身),这样更能够代表一个活动的系统,评估相对于平均热时间的性能收益将会提供一个繁忙系统上对性能收益的期望。
实例:在数据库people中创建people和boysnames两张表,代码如下:
CREATE DATABASE [people] ON PRIMARY
( NAME = N'people',
FILENAME = N'C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL.1\MSSQL\DATA\people.mdf' ,
SIZE = 409600KB , MAXSIZE = UNLIMITED, FILEGROWTH = 10240KB )
LOG ON
( NAME = N'people_log',
FILENAME = N'C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL.1\MSSQL\DATA\people_log.ldf' ,
SIZE = 10240KB , MAXSIZE = 102400KB , FILEGROWTH = 10240KB )
GO
CREATE TABLE people
(
personId UNIQUEIDENTIFIER DEFAULT newsequentialid(),
firstname VARCHAR(80) not null,
lastname VARCHAR(80) not null,
dob DATETIME not null,
dod DATETIME null,
sex CHAR(1) not null
)
go
CREATE TABLE boysnames
(
ID INT IDENTITY(0,1) not null,
[name] VARCHAR(80) not null
)
Go
分别为这两张表插入10000条记录,代码如下:
declare @i int
set @i=1
while @i <10000
begin
insert into people values(@i,'abc','123','1')
set @i=@i+1
end
declare @i int
set @i=1
while @i <10000
begin
insert into boysnames values(@i,'0')
set @i=@i+1
end
现在通过统计信息来统计一个查询语句的执行期间的等待时间,代码如下:
use People
go
-- *********************************************
--
-- WARNING This script empties the people table and fills it with just 8 people!!!
--
-- *********************************************
truncate table people
go
dbcc dropcleanbuffers
dbcc freeproccache
go
-- either do stats time and stats IO, OR showplan_text. Using all three makes he OP a little hard to read!
set statistics time on
set statistics io on
go
-- set showplan_text on
-- go
-- Cold run
select * from people
where personid = (select id from boysnames where name = '123')
go
-- first warm run
select * from people
where personid = (select id from boysnames where name = '123')
go
-- second warm run
select * from people
where personid = (select id from boysnames where name = '123')
go
-- third warm run
select * from people
where personid = (select id from boysnames where name = '123')
go
-- set showplan_text off
set statistics time off
set statistics io off
go
-- we ran the SP to insert 2 people 4 times, so there will be 8 people in the DB
select count (*) from people
go
执行该过程的结果如下:
DBCC execution completed. If DBCC printed error messages, contact your system administrator.
DBCC execution completed. If DBCC printed error messages, contact your system administrator.
SQL Server Execution Times:
CPU time = 0 ms, elapsed time = 0 ms.
SQL Server Execution Times:
CPU time = 0 ms, elapsed time = 0 ms.
SQL Server parse and compile time:
CPU time = 15 ms, elapsed time = 31 ms.
Table 'people'. Scan count 1, logical reads 0, physical reads 0, read-ahead reads 0.
Table 'boysnames'. Scan count 1, logical reads 26, physical reads 0, read-ahead reads 26.
SQL Server Execution Times:
CPU time = 0 ms, elapsed time = 64 ms.
(0 行受影响)
SQL Server parse and compile time:
CPU time = 0 ms, elapsed time = 1 ms.
Table 'people'. Scan count 1, logical reads 0, physical reads 0, read-ahead reads 0.
Table 'boysnames'. Scan count 1, logical reads 26, physical reads 0, read-ahead reads 0.
SQL Server Execution Times:
CPU time = 0 ms, elapsed time = 1 ms.
(0 行受影响)
SQL Server parse and compile time:
CPU time = 0 ms, elapsed time = 1 ms.
Table 'people'. Scan count 1, logical reads 0, physical reads 0, read-ahead reads 0.
Table 'boysnames'. Scan count 1, logical reads 26, physical reads 0, read-ahead reads 0.
SQL Server Execution Times:
CPU time = 0 ms, elapsed time = 1 ms.
(0 行受影响)
SQL Server parse and compile time:
CPU time = 0 ms, elapsed time = 1 ms.
Table 'people'. Scan count 1, logical reads 0, physical reads 0, read-ahead reads 0.
Table 'boysnames'. Scan count 1, logical reads 26, physical reads 0, read-ahead reads 0.
SQL Server Execution Times:
CPU time = 0 ms, elapsed time = 1 ms.
(0 行受影响)
SQL Server parse and compile time:
CPU time = 0 ms, elapsed time = 0 ms.
分析输出信息可以发现,冷运行共用时64秒,热运行共用时1秒,冷运行中共进行了26次逻辑读操作,主要对是boysnames进行了逻辑读操作。
接下来使用DTA对查询语句进行分析,需要分析的语句如下:
select * from people
where personid = (select id from boysnames where name = '123')
将分析语句保存为后缀名为.sql的文件,单击开始菜单->所有程序->Microsoft SQL Server 2005,选择性能工具中的数据库引擎优化顾问,或在Micosoft SQL Server Management Studio主界面中单击工具菜单,在下位菜单中选择数据库引擎优化顾问选项,弹出如图11-43所示的连接对话框。
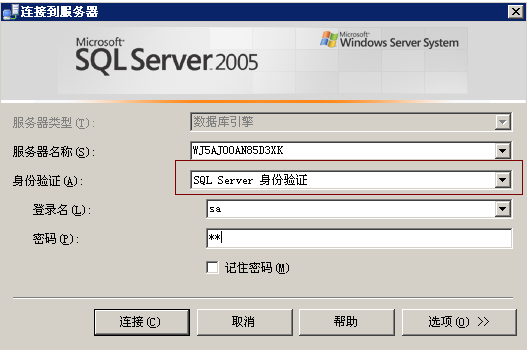
图11-43 连接数据库服务器
注意:身份验证方式使用SQL Server身份验证,不能使用Windows身份验证,否则分析过程中会出错。
连接成功后进入DTA主界面,工作负荷的方式选择为文件,单击【】按钮可以设置待分析的文件,同时选择用于工作负荷分析的数据库,如图11-44所示。

图11-44 设置工作负荷
单击左上角的开始分析按钮【】 ,如图11-45所示。
图11-45 开始分析
分析完成后,DTA会给出优化的评估建议。
本章主要介绍了关于“性能测试—用DTA调校索引”的内容,大家喜欢的话记得每天来这里和小编一起学习涨薪技能哦。(笔芯)
附:川石信息全国校区最新开班时间,课程资料获取13691729932(微信同号)。